數據科學學院師生26篇論文被頂級國際會議NeurIPS 2023接收
香港中文大學(深圳)數據科學學院師生共26篇論文被機器學習和計算神經科學領域的頂級國際會議NeurIPS (Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems?神經信息處理系統大會, 簡稱NeurIPS或NIPS)?2023接收。論文來自學院18位教授、1位博士后及10位博士生、1位碩士生,除研究生外,學院的本科生也積極參與科研,論文作者中還包括2位學院本科生。NeurIPS 2023的接收率為26.1%。
2位本科生:
盧藝文、施展
?
1位碩士生:
晏志遠
?
10位博士生:
董婧、李子牛、路舜麟、喬冠仁、孫子恒、王遠程、魏少魁、楊超、張明達、朱明麗
?
1位博士后:
李文浩
?
18位教授:
丁宏強、樊繼聰、李彤欣、李海洲、李爽、李文燁、李肖、劉桂良、羅智泉、馬晨昊、茅劍鋒、孫若愚、王趵翔、王本友、吳保元、武執政、查宏遠、張瑞茂
?

?
NeurlPS簡介
神經信息處理系統大會(NeurIPS/NIPS)是機器學習和計算神經科學領域的頂尖國際會議。在中國計算機學會的國際學術會議排名中,NeurIPS是人工智能領域的A類學術會議。大會討論的內容包含深度學習、計算機視覺、大規模機器學習、學習理論、優化、稀疏理論等眾多細分領域。該會議固定在每年的12月舉行, 由NIPS基金會主辦,今年是該會議舉辦的第37屆,將于12月10日至12月16日在美國新奧爾良會議中心舉行。
?
來源:NeurIPS官網、百度百科
?
更多學生信息,詳見:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/fmn4Lxc7bl1EAM17Xf1Zcg
26篇論文詳情?
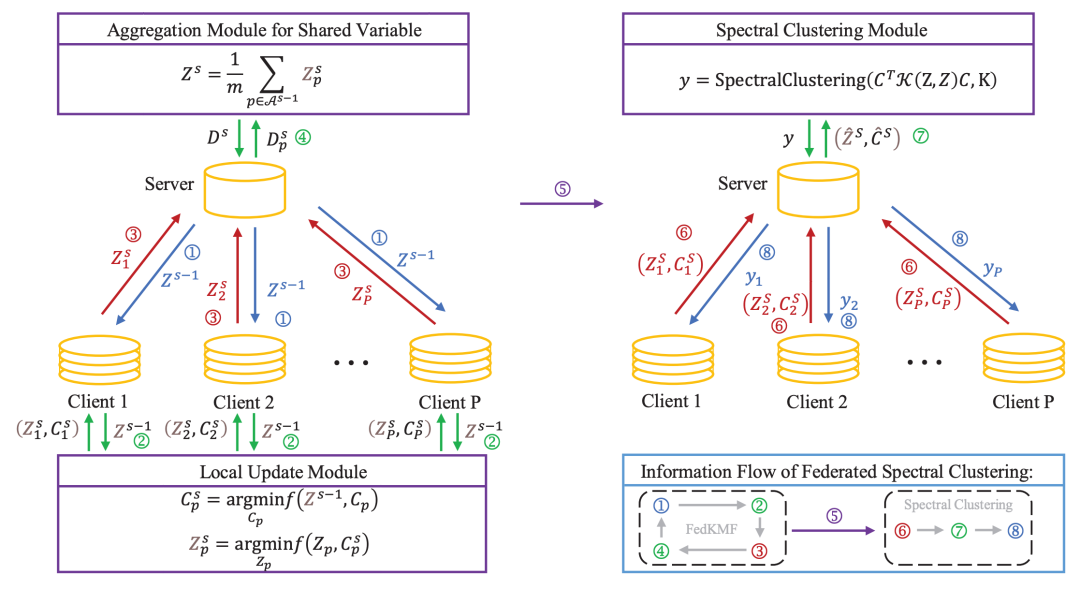
1.?Federated Spectral Clustering via Secure Similarity Reconstruction
作者:
Dong Qiao,?Chris Ding, Jicong Fan
簡介:
聯邦學習在保護數據隱私上具有優勢。自谷歌提出聯邦學習的概念以來,有很多基于聯邦學習框架的安全學習算法已經被提出,以應對數據泄露和信息安全威脅帶來的挑戰。無監督學習在實際生產中有著廣泛的應用。然而,回顧現有的文獻,我們發現相關的研究,特別是關于聚類的聯邦學習研究,還較少。在這篇文章中,我們提出了一個基于核函數因子分解的聯邦譜聚類方法,用于分布式數據的安全聚類。我們基于聯邦學習的基本框架,隱式地構建了一個近似的相似度矩陣。基于該相似度矩陣,我們的方法能夠在不直接獲取終端敏感數據的情況下執行譜聚類任務。為了說明所提算法的有效性,我們證明了算法的收斂性、相似度重構的殘差上界以及保證聚類結果的充分條件。除此之外,我們也證明了所提算法可以通過加噪音的方式滿足差分隱私。合成數據集和真實數據集上的實驗結果顯示我們的算法是有效且可比的。
Abstracts:
Federated learning has a significant advantage in protecting data and information privacy. Many scholars proposed various secure learning methods within the framework of federated learning but the study on secure federated unsupervised learning especially clustering is limited. We in this work propose a secure kernelized factorization method for federated spectral clustering on distributed data. The method is non-trivial because the kernel or similarity matrix for spectral clustering is computed by data pairs, which violates the principle of privacy protection. Our method implicitly constructs an approximation for the kernel matrix on distributed data such that we can perform spectral clustering under the constraint of privacy protection. We provide a convergence guarantee of the optimization algorithm, a reconstruction error bound of the Gaussian kernel matrix, and the sufficient condition of correct clustering of our method. We also present guarantees of differential privacy. Numerical results on synthetic and real datasets demonstrate that the proposed method is efficient and accurate in comparison to the baselines.
?
?
鏈接:
https://nips.cc/virtual/2023/poster/71656
?
?
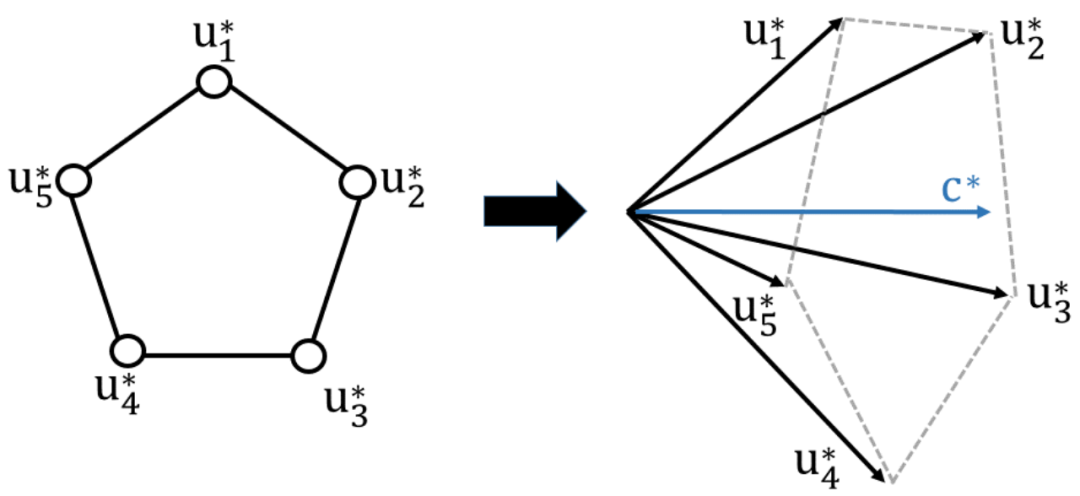
2.?Lovász Principle for Unsupervised Graph Representation Learning
作者:
Ziheng Sun (SDS博士生), Chris Ding, Jicong Fan
簡介:
本文側重于圖級表示學習,旨在將圖表示為可直接用于圖分類等下游任務的向量。我們受到了圖論中Lovász數的啟發并提出了一種名為Lovász原理的新型圖級表示學習原理。Lovász數是一個實數,是圖Shannon容量的上界,與圖的各種全局特征密切相關。具體而言,我們展示了用于計算Lovász數的傘柄向量可能是圖表示的合適選擇,因為它捕捉了圖的全局特性。為了處理直接應用傘柄向量帶來的困難和問題,我們將Lovász原理應用于圖神經網絡來解決這些問題。此外,我們提出了一個增強版的Lovász原理來更高效地利用子圖的Lovász數。實驗證明,我們的Lovász原理在無監督和半監督圖級表示學習任務中與基線方法相比取得了具有競爭力的表現。
Abstracts:
This paper focuses on graph-level representation learning that aims to represent graphs as vectors that can be directly utilized in downstream tasks such as graph classification. We propose a novel graph-level representation learning principle called Lovász principle, which is motivated by the Lovász number in graph theory. The Lovász number is a real number that is an upper bound for graph Shannon capacity and is strongly connected with various global characteristics of graph. Specifically, we show that the handle vector for computing the Lovász number is potentially a suitable choice for graph representation, as it captures a graph's global properties, though a direct application of the handle vector is difficult and problematic. We propose to use neural networks to address the problems and hence provide the Lovász principle. Moreover, we propose an enhanced Lovász principle that is able to exploit the subgraph Lovász numbers directly and efficiently. The experiments demonstrate that our Lovász principles achieve competitive performance compared to the baselines in unsupervised and semi-supervised graph-level representation learning tasks.
?
鏈接:
https://nips.cc/virtual/2023/poster/73041
?
?
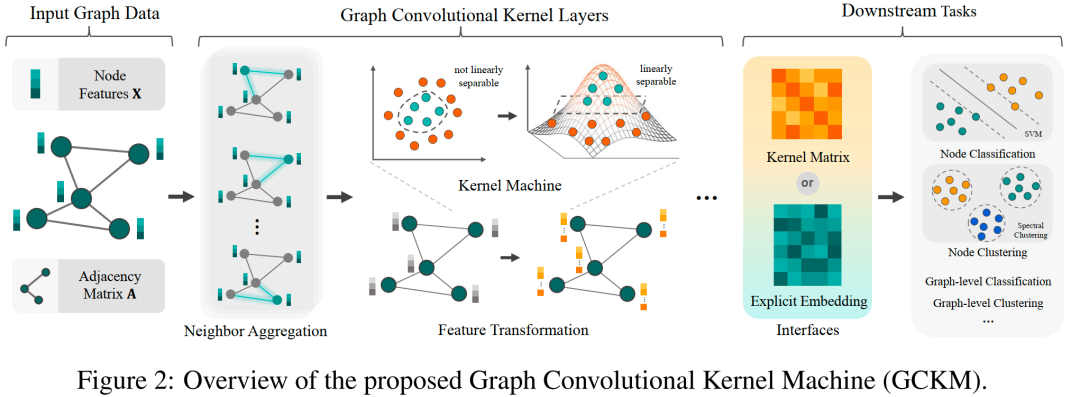
3.?Graph Convolutional Kernel Machine versus Graph Convolutional Networks
作者:
Zhihao Wu, Zhao Zhang,?Jicong Fan
簡介:
具有一兩個隱藏層的圖卷積網絡(GCN)已廣泛用于處理各個學科中普遍存在的圖數據。許多研究表明,使 GCN 更深的增益很小,甚至是負的。這意味著圖數據的復雜性通常是有限的,淺層模型通常足以提取節點分類等各種任務的表達特征。因此,在這項工作中,我們提出了一個稱為圖卷積核機(GCKM)的框架,用于基于圖的機器學習。GCKM 建立在與圖卷積集成的核函數之上。一個例子是用于節點分類的圖卷積核支持向量機(GCKSVM),我們分析了泛化誤差界并討論了圖結構的影響。與 GCN 相比,GCKM 在架構設計、超參數調整和優化方面需要更少的工作。更重要的是,GCKM保證獲得全局最優解,并且具有很強的泛化能力和高可解釋性。GCKM 是可組合的,可以擴展到大規模數據,并且適用于各種任務(例如,節點或圖分類、聚類、特征提取、降維)。基準數據集上的數值結果表明,除了上述優點之外,GCKM 與 GCN 相比至少具有有競爭力的準確性。
Abstracts:
Graph convolutional networks (GCN) with one or two hidden layers have been widely used in handling graph data that are prevalent in various disciplines. Many studies showed that the gain of making GCNs deeper is tiny or even negative. This implies that the complexity of graph data is often limited and shallow models are often sufficient to extract expressive features for various tasks such as node classification. Therefore, in this work, we present a framework called graph convolutional kernel machine (GCKM) for graph-based machine learning. GCKMs are built upon kernel functions integrated with graph convolution. An example is the graph convolutional kernel support vector machine (GCKSVM) for node classification, for which we analyze the generalization error bound and discuss the impact of the graph structure. Compared to GCNs, GCKMs require much less effort in architecture design, hyperparameter tuning, and optimization. More importantly, GCKMs are guaranteed to obtain globally optimal solutions and have strong generalization ability and high interpretability. GCKMs are composable, can be extended to large-scale data, and are applicable to various tasks (e.g., node or graph classification, clustering, feature extraction, dimensionality reduction). The numerical results on benchmark datasets show that, besides the aforementioned advantages, GCKMs have at least competitive accuracy compared to GCNs.
鏈接:
https://nips.cc/virtual/2023/poster/71620
?
?
4.?Boosting Spectral Clustering on Incomplete Data via Kernel Correction and Affinity Learning
作者:
Fangchen Yu,?Runze Zhao,?Zhan Shi (SDS本科生),?Yiwen Lu (SDS本科生), Jicong Fan, Yicheng Zeng,?Jianfeng Mao,?Wenye Li
簡介:
譜聚類方法因其簡單性和有效性在非凸數據的聚類中備受歡迎。在譜聚類中,相似性度量衡量數據樣本之間的局部近鄰關系,使用高質量的相似性度量對構建有效的相似性圖是非常重要的。然而,缺失數據可能導致不準確的相似性度量,從而降低聚類性能。為了解決這些問題,我們提出了一個無插補的框架,和兩類新穎的方法來改進缺失數據上的譜聚類。首先,我們引入了一種新的核校正方法,該方法增強了對缺失數據估計的核矩陣的質量,且具有理論保證,從而使基于預定義核的經典譜聚類受益。其次,我們開發了一系列新的相似性學習方法,基于自表達框架和Lp-范數,并構建具有自適應擴展的內稟相似性矩陣。我們的方法在基準數據集上超越了現有的數據插補和距離校準技術,為各種實際應用中缺失數據的譜聚類提供了有前景的解決方案。
Abstracts:
Spectral clustering has gained popularity for clustering non-convex data due to its simplicity and effectiveness. It is essential to construct a similarity graph using a high-quality affinity measure that models the local neighborhood relations among data samples. However, incomplete data can lead to inaccurate affinity measures, resulting in degraded clustering performance. To address these issues, we propose an imputation-free framework with two novel approaches to improve spectral clustering on incomplete data. Firstly, we introduce a new kernel correction method that enhances the quality of the kernel matrix estimated on incomplete data with a theoretical guarantee, benefiting classical spectral clustering on pre-defined kernels. Secondly, we develop a series of new affinity learning methods that equips the self-expressive framework with Lp-norm to construct an intrinsic affinity matrix with adaptive extensions. Our methods outperform existing data imputation and distance calibration techniques on benchmark datasets, offering a promising solution to spectral clustering on incomplete data in various real-world applications.
https://nips.cc/virtual/2023/poster/70019
?
?
5.?Anytime-Constrained Reinforcement Learning with Policy Prior
作者:
Jianyi Yang, Pengfei Li,?Tongxin Li,?Adam Wierman, Shaolei Ren
簡介:
本文研究了“隨時約束馬爾可夫決策過程”(A-CMDP)問題。現有關于約束馬爾可夫決策過程(CMDPs)的研究目標是在隨機動態中優化預期獎勵,同時約束預期成本,但在具體的特定時刻中,成本仍可能過高且不盡人意。相對而言,A-CMDP的目標是在每輪任何時刻中保證有界成本的前提下,優化預期獎勵,以應對策略先驗。論文提出了一種新的算法,名為“隨時約束強化學習”(ACRL),并可靠地確保了隨時的成本約束。遺憾分析理論顯示,該策略在隨時約束下會漸近地匹配最優獎勵。此外,關于碳智能計算的應用實驗證實了ACRL在獎勵性能和成本約束保證方面的有效性。
Abstracts:
This paper studies the problem of Anytime-Constrained Markov Decision Process (A-CMDP). Existing works on Constrained Markov Decision Processes (CMDPs) aim to optimize the expected reward while constraining the expected cost over random dynamics, but the cost in a specific episode can still be unsatisfactorily high. In contrast, the goal of A-CMDP is to optimize the expected reward while guaranteeing a bounded cost in each round of any episode against a policy prior.? We propose a new algorithm, called Anytime-Constrained Reinforcement Learning (ACRL), which provably guarantees the anytime cost constraints. The regret analysis shows the policy asymptotically matches the optimal reward achievable under anytime constraints. Experiments on the application of carbon-intelligent computing verify the reward performance and cost constraint guarantee of ACRL.
?
?
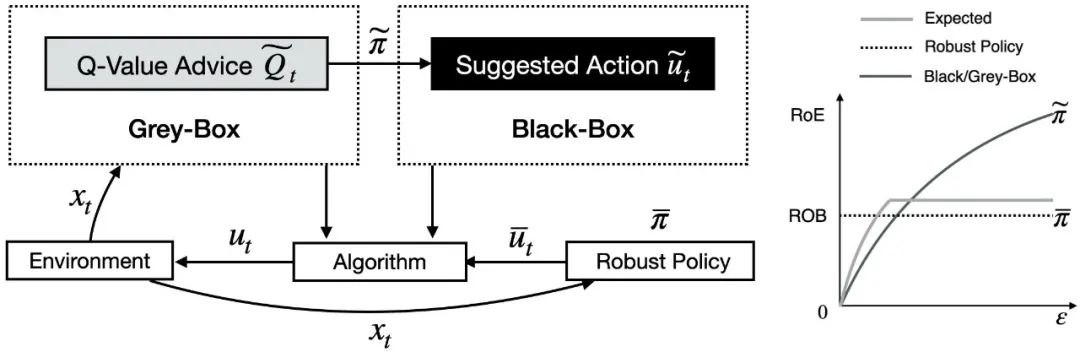
6.?Beyond Black-Box Advice: Learning-Augmented Algorithms for MDPs with Q-Value Predictions
作者:
Tongxin Li, Yiheng Lin, Shaolei Ren, Adam Wierman
簡介:
本文在單軌跡時變馬爾可夫決策過程(MDP)的背景下,深入探討了一致性與魯棒性之間的理論權衡,特別是在處理不受信任的機器學習建議的情境中。與一般以來自黑盒的建議處理方式不同,研究考慮了一個灰箱環境,在這個環境中,不僅有黑盒決策,也可以獲得黑盒決策生成時的附加信息。論文在一個包含連續與離散狀態/動作空間的廣義MDP模型下,基于不可信Q價值函數建議,證明了一種具有創新性的一致性與魯棒性權衡。論文研究結果凸顯了,利用Q價值函數灰箱模型可以實現機器學習建議與魯棒基線之間的動態平衡,因此可以獲得接近最優的性能保證。在理論上超越了僅依賴黑箱建議所能實現的性能。
Abstracts:
We study the tradeoff between consistency and robustness in the context of a single-trajectory time-varying Markov Decision Process (MDP) with untrusted machine-learned advice. Our work departs from the typical approach of treating advice as coming from black-box sources by instead considering a setting where additional information about? how the advice is generated is available. We prove a first-of-its-kind consistency and robustness tradeoff given Q-value advice under a general MDP model that includes both continuous and discrete state/action spaces. Our results highlight that utilizing Q-value advice enables dynamic pursuit of the better of machine-learned advice and a robust baseline, thus result in near-optimal performance guarantees, which provably improves what can be obtained solely with black-box advice.
鏈接:
https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.10524
?
?
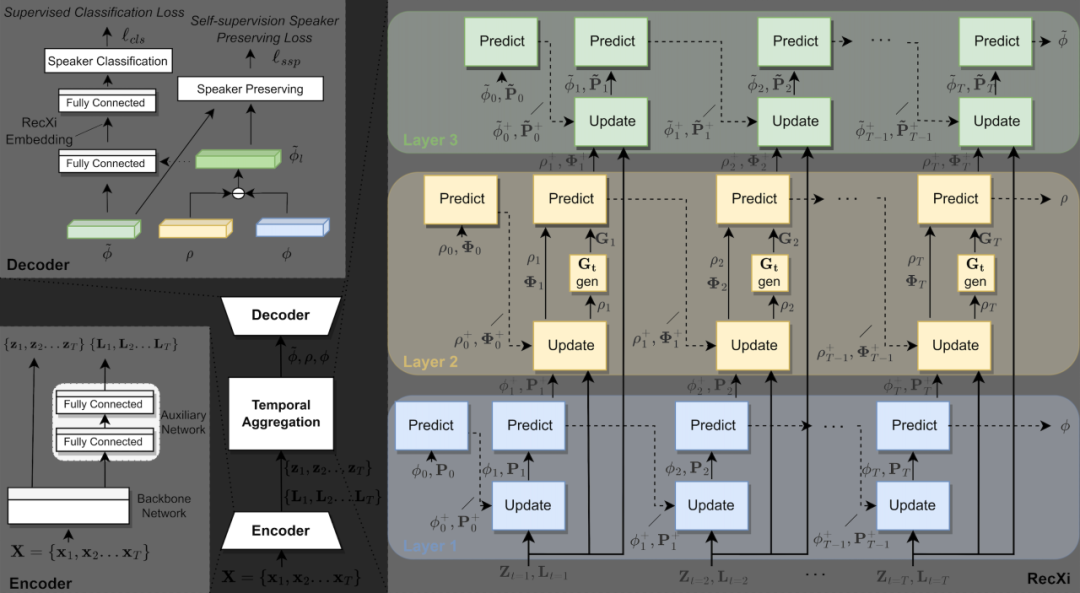
7.?Disentangling Voice and Content with Self-Supervision for Speaker Recognition
作者:
Tianchi Liu, Kong Aik Lee, Qiongqiong Wang,?Haizhou Li
簡介:
針對說話者識別,由于語音中混合了說話者特征和內容,因此從語音中提取準確的說話者表示是困難的。本文提出了一個同時建模語音中說話者特征和內容變異性的解耦框架。這一框架通過三個高斯推斷層實現,每個推斷層都包括一個可學習的transition模型,用于提取不同的語音成分。值得注意的是,我們專門設計了一個強化的transition模型,用于建模復雜的語音動態。我們還提出了一種自監督方法,可以在沒有除說話者身份之外的標簽的情況下動態解耦內容。所提出的框架的有效性通過在VoxCeleb和SITW數據集上進行的實驗進行驗證,其中EER和minDCF平均降低了分別為9.56%和8.24%。由于不需要額外的模型訓練或數據,因此它在實際應用中易于使用。
Abstracts:
For speaker recognition, it is difficult to extract an accurate speaker representation from speech because of its mixture of speaker traits and content. This paper proposes a disentanglement framework that simultaneously models speaker traits and content variability in speech. It is realized with the use of three Gaussian inference layers, each consisting of a learnable transition model that extracts distinct speech components. Notably, a strengthened transition model is specifically designed to model complex speech dynamics. We also propose a self-supervision method to dynamically disentangle content without the use of labels other than speaker identities. The efficacy of the proposed framework is validated via experiments conducted on the VoxCeleb and SITW datasets with 9.56% and 8.24% average reductions in EER and minDCF, respectively. Since neither additional model training nor data is specifically needed, it is easily applicable in practical use
?
?
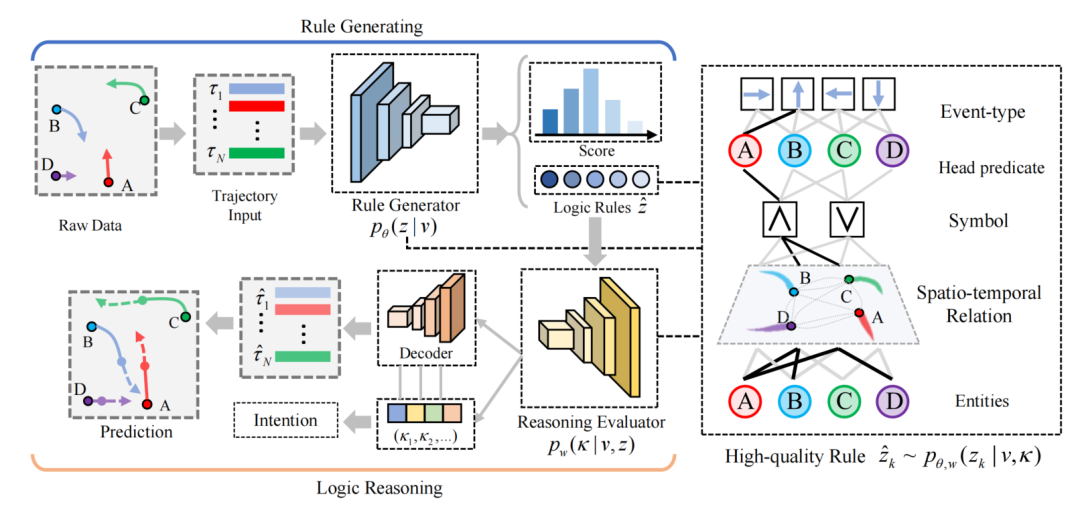
8.?Discovering Intrinsic Spatial-Temporal Logic Rules to Explain Human Actions.
作者:
Chengzhi Cao,?Chao Yang (SDS博士生), Ruimao Zhang, Shuang Li
簡介:
我們通過分析人類運動的軌跡,提出了一個基于邏輯的知識驅動的人類運動建模框架。我們的方法受到這樣一個事實的啟發,即人類的行為通常由他們的意圖或欲望驅動,并受到環境因素的影響,如與周圍物體的空間關系。在本文中,我們引入了一組時空邏輯規則作為解釋人類行為的知識。這些規則將從觀測數據中自動發現。為了學習模型參數和規則內容,我們設計了一種期望最大化(EM)算法,該算法將規則內容視為潛在變量。EM算法在E步和M步之間交替:在E步中,評估潛在規則內容上的后驗分布;在M步驟中,通過最大化當前期望的對數似然性來聯合優化規則生成器和模型參數。我們的模型可能在體育分析、機器人和自動駕駛汽車等領域有廣泛的應用,在這些領域,理解人類運動至關重要。我們在行人和NBA籃球運動員數據集上展示了該模型優越的可解釋性和預測性能,兩者都取得了有希望的結果。
Abstracts:
We propose a logic-informed knowledge-driven modeling framework for human 1 movements by analyzing their trajectories. Our approach is inspired by the fact that 2 human actions are usually driven by their intentions or desires, and are influenced 3 by environmental factors such as the spatial relationships with surrounding objects. 4 In this paper, we introduce a set of spatial-temporal logic rules as knowledge 5 to explain human actions. These rules will be automatically discovered from 6 observational data. To learn the model parameters and the rule content, we design 7 an expectation-maximization (EM) algorithm, which treats the rule content as 8 latent variables. The EM algorithm alternates between the E-step and M-step: 9 in the E-step, the posterior distribution over the latent rule content is evaluated; 10 in the M-step, the rule generator and model parameters are jointly optimized by 11 maximizing the current expected log-likelihood. Our model may have a wide 12 range of applications in areas such as sports analytics, robotics, and autonomous 13 cars, where understanding human movements are essential. We demonstrate the 14 model’s superior interpretability and prediction performance on pedestrian and 15 NBA basketball player datasets, both achieving promising results.
鏈接:
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2306.12244
?
?
9.?ReSync: Riemannian Subgradient-based Robust Rotation Synchronization
作者:
Huikang Liu,?Xiao Li,?Anthony Man-Cho So.
簡介:
本文介紹了ReSync,這是一個基于黎曼梯度的算法,用于解決在各種工程應用中出現的魯棒旋轉同步問題。ReSync解決了在旋轉群上的最小非平方最小化公式,該公式是非光滑且非凸的,并且旨在直接恢復潛在的旋轉。在隨機損壞設置下為ReSync提供了強大的理論保證。具體來說,首先證明ReSync的初始化程序產生了一個位于地面真實旋轉周圍局部區域的合適初始點,接著建立了上述公式的弱銳度性質,然后利用這個性質推導出ReSync對地面真實旋轉的局部線性收斂性。通過結合這些保證,得出ReSync在適當條件下線性收斂到地面真實旋轉的結論。實驗結果證明了ReSync的有效性。
Abstracts:
This work presents ReSync, a Riemannian subgradient-based algorithm for solving the robust rotation synchronization problem, which arises in various engineering applications. ReSync solves a least-unsquared minimization formulation over the rotation group, which is nonsmooth and nonconvex, and aims at recovering the underlying rotations directly. We provide strong theoretical guarantees for ReSync under the random corruption setting. Specifically, we first show that the initialization procedure of ReSync yields a proper initial point that lies in a local region around the ground-truth rotations. We next establish the weak sharpness property of the aforementioned formulation and then utilize this property to derive the local linear convergence of ReSync to the ground-truth rotations. By combining these guarantees, we conclude that ReSync converges linearly to the ground-truth rotations under appropriate conditions. Experiment results demonstrate the effectiveness of ReSync.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.15136
?
?
10.?An Alternative to Variance: Gini Deviation for Risk-averse Policy Gradient.
作者:
Yudong Luo,?Guiliang Liu,?Pascal Poupart, Yangchen Pan
簡介:
將策略回報的方差限制在一定范圍內是風險規避強化學習(RL)中的常見選擇,因為它有清晰的數學定義和易于解釋的特性。傳統方法直接限制總回報的方差。最近的方法將每步獎勵的方差作為替代。我們深入研究了這些基于方差的方法的局限性,例如對數值規模的敏感性和阻礙策略學習,并建議使用另一種風險度量,Gini偏差,作為替代。我們研究了這種新的風險度量的各種屬性,并推導出一種策略梯度算法來最小化它。在風險規避可以明確定義的領域進行的實證評估表明,我們的算法可以緩解基于方差的風險度量的局限性,并在其他算法無法學習到合理策略的情況下,以方差和Gini偏差的低風險獲得高回報。
Abstracts:
Restricting the variance of a policy’s return is a popular choice in risk-averse Reinforcement Learning (RL) due to its clear mathematical definition and easy interpretability. Traditional methods directly restrict the total return variance. Recent methods restrict the per-step reward variance as a proxy. We thoroughly examine the limitations of these variance-based methods, such as sensitivity to numerical scale and hindering of policy learning, and propose to use an alternative risk measure, Gini deviation, as a substitute. We study various properties of this new risk measure and derive a policy gradient algorithm to minimize it. Empirical evaluation in domains where risk-aversion can be clearly defined, shows that our algorithm can mitigate the limitations of variance-based risk measures and achieves high return with low risk in terms of variance and Gini deviation when others fail to learn a reasonable policy.
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2307.08873.pdf
?
?
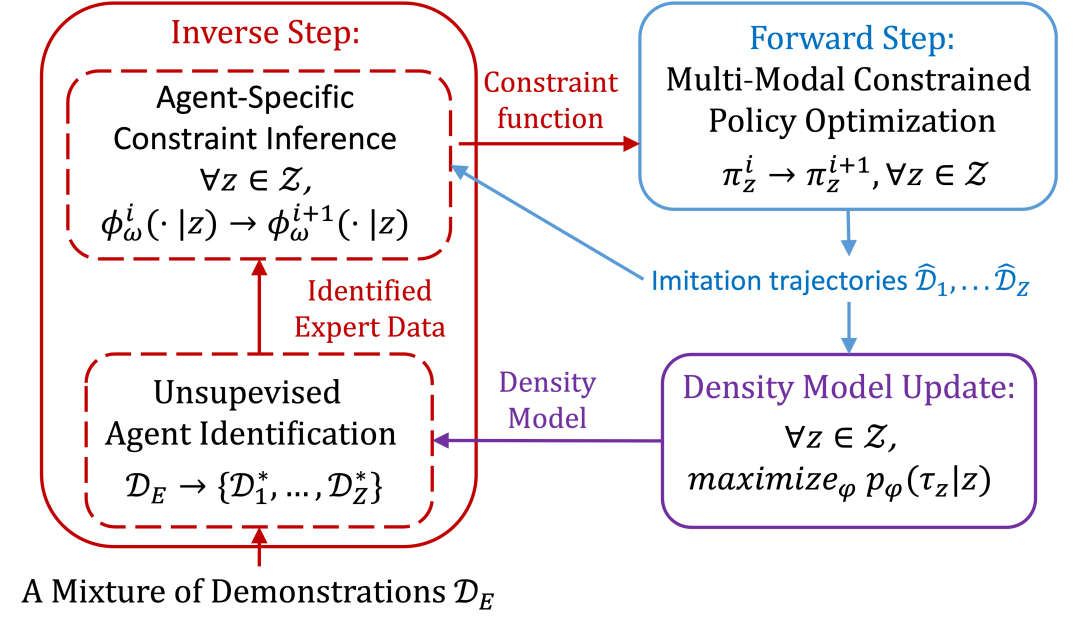
11.?Multi-Modal Inverse Constrained Reinforcement Learning from a Mixture of Demonstrations
作者:
Guanren Qiao (SDS博士生), Guiliang Liu,?Pascal Poupart, Zhiqiang Xu
簡介:
逆向約束強化學習(Inverse Constraint Reinforcement Learning,ICRL)旨在以數據驅動的方式恢復專家代理遵循的基本約束。現有的ICRL算法通常假設示范數據由單一類型的專家生成。然而,在實踐中,示范通常包含從遵循不同約束的各種專家代理收集的軌跡的混合,這使得用統一的約束函數解釋專家行為變得具有挑戰性。為了解決這個問題,我們提出了一種多模式逆向約束強化學習(Multi-Modal Inverse Constrained Reinforcement Learning,MMICRL)算法,用于同時估計對應于不同類型專家的多個約束。MMICRL構建了一個基于流的密度估計器,從示范中實現了無監督的專家識別,以推斷特定于代理的約束。根據這些約束,MMICRL使用一種新穎的多模式約束策略優化目標來模仿專家策略,該目標最小化了代理條件下的策略熵并最大化了無條件的策略熵。為了增強魯棒性,我們將這個目標納入對比學習框架中。這種方法使得模仿策略能夠捕捉到專家代理之間的行為多樣性。在離散和連續環境中進行的大量實驗證明,MMICRL在約束恢復和控制性能方面優于其他基線算法。
Abstracts:
Inverse Constraint Reinforcement Learning (ICRL) aims to recover the underlying constraints respected by expert agents in a data-driven manner. Existing ICRL algorithms typically assume that the demonstration data is generated by a single type of expert. However, in practice, demonstrations often comprise a mixture of trajectories collected from various expert agents respecting different constraints, making it challenging to explain expert behaviors with a unified constraint function. To tackle this issue, we propose a Multi-Modal Inverse Constrained Reinforcement Learning (MMICRL) algorithm for simultaneously estimating multiple constraints corresponding to different types of experts. MMICRL constructs a flow-based density estimator that enables unsupervised expert identification from demonstrations, so as to infer the agent-specific constraints. Following these constraints, MMICRL imitates expert policies with a novel multi-modal constrained policy optimization objective that minimizes the agent-conditioned policy entropy and maximizes the unconditioned one. To enhance robustness, we incorporate this objective into the contrastive learning framework. This approach enables imitation policies to capture the diversity of behaviors among expert agents. Extensive experiments in both discrete and continuous environments show that MMICRL outperforms other baselines in terms of constraint recovery and control performance.
?
?
12.?PAC-Bayesian Spectrally-Normalized Bounds for Adversarially Robust Generalization
作者:
Jiancong Xiao,?Ruoyu Sun, Zhi-Quan Luo
簡介:
深度神經網絡(DNNs)容易受到對抗性攻擊。經驗發現,對抗性魯棒泛化在建立對抗性攻擊的防御算法中至關重要。因此,研究魯棒泛化的理論保證是有趣的。本文重點研究 PAC-Bayes 分析(Neyshabur 等人,2017b)。主要的挑戰在于將標準設置中的一個關鍵成分,即權重擾動界限,擴展到魯棒設置中。現有的嘗試嚴重依賴額外的強假設,導致界限寬松。在本文中,我們解決了這個問題,并為 DNNs 提供了一個光譜歸一化的魯棒泛化界限。我們的界限至少與標準的泛化界限一樣緊密,只是在擾動強度 $\epsilon$ 的一個因子上有所不同。與現有的魯棒泛化界限相比,我們的界限有兩個顯著的優點:1)它不依賴額外的假設,和 2)它明顯更為緊密。我們提出了一個框架,使我們能夠得出更為普遍的結果。具體來說,我們將主要結果擴展到 1)對抗一般非-$\ell_p$ 攻擊的魯棒性,和 2)其他神經網絡架構,如 ResNet。
Abstracts:
Deep neural networks (DNNs) are vulnerable to adversarial attacks. It is found empirically that adversarially robust generalization is crucial in establishing defense algorithms against adversarial attacks. Therefore, it is interesting to study the theoretical guarantee of robust generalization. This paper focuses on PAC-Bayes analysis (Neyshabur et al., 2017b). The main challenge lies in extending the key ingredient, which is a weight perturbation bound in standard settings, to the robust settings. Existing attempts heavily rely on additional strong assumptions, leading to loose bounds. In this paper, we address this issue and provide a spectrally-normalized robust generalization bound for DNNs. Our bound is at least as tight as the standard generalization bound, differing only by a factor of the perturbation strength $\epsilon$. In comparison to existing robust generalization bounds, our bound offers two significant advantages: 1) it does not depend on additional assumptions, and 2) it is considerably tighter. We present a framework that enables us to derive more general results. Specifically, we extend the main result to 1) adversarial robustness against general non-$\ell_p$ attacks, and 2) other neural network architectures, such as ResNet.
?
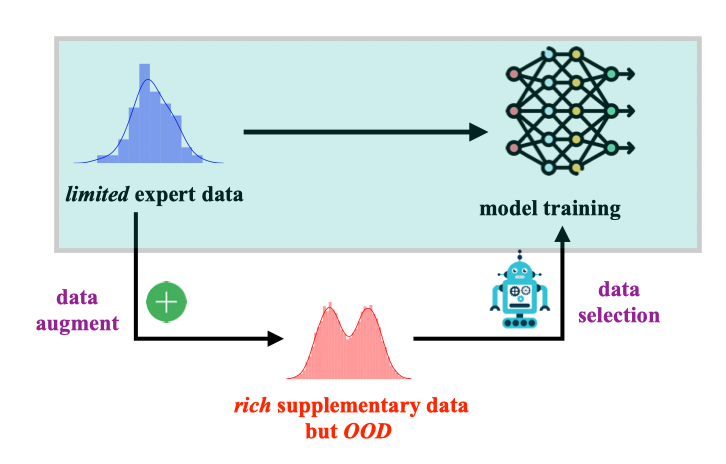
13.?Imitation Learning from Imperfection: Theoretical Justifications and Algorithms
作者:
Ziniu Li (SDS博士生),?Tian Xu, Zeyu Qin, Yang Yu,?Zhi-Quan Luo
簡介:
模仿學習(IL)算法擅長于從專家數據中獲取高質量的策略,以處理順序決策任務。但是,當面臨專家數據有限的情況時,它們的效果會受到阻礙。為了應對這個挑戰,出現了一種名為(離線)IL與補充數據的新框架,通過整合一個額外但不完美的數據集來增強學習,該數據集是從次優策略中低成本獲取的。然而,由于可能包含了超出專家分布的樣本,學習變得具有挑戰性。在這項工作中,我們首次對這個框架進行了數學形式化,揭示了它的限制。我們的理論分析顯示,一個簡單的方法——將行為克隆(BC)算法的概念應用于合并的專家和補充數據集——可能不及只依賴專家數據的普通BC算法。這個不足是由于兩個數據源之間的分布偏移造成的。為了解決這個問題,我們提出了一種新的基于重要性抽樣的技術,用于選擇專家分布內的數據。我們證明,所提出的方法理論上消除了簡單方法的差距,突顯了在處理不完美數據時的效果。實證研究表明,我們的方法在包括機器人運動控制、Atari視頻游戲和圖像分類在內的任務中,超越了先前的最先進方法。總的來說,我們的工作強調了通過有效的數據選擇利用多樣化數據源來改善模仿學習的潛力。
Abstracts:
Imitation learning (IL) algorithms excel in acquiring high-quality policies from expert data for sequential decision-making tasks. But, their effectiveness is hampered when faced with limited expert data. To tackle this challenge, a novel framework called (offline) IL with supplementary data has emerged, which enhances learning by incorporating an additional yet imperfect dataset obtained inexpensively from sub-optimal policies. Nonetheless, learning becomes challenging due to the potential inclusion of out-of-expert-distribution samples. In this work, we pioneer the mathematical formalization of this framework, uncovering its limitations. Our theoretical analysis reveals that a naive approach—applying the behavioral cloning (BC) algorithm concept to the combined set of expert and supplementary data—may fall short of vanilla BC, which solely relies on expert data. This deficiency arises due to the distribution shift between the two data sources. To address this issue, we propose a new importance-sampling-based technique for selecting data within the expert distribution. We prove that the proposed method theoretically eliminates the gap of the naive approach, highlighting its efficacy when handling imperfect data. Empirical studies demonstrate that our method outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods in tasks including robotics locomotion control, Atari video games, and image classification. Overall, our work underscores the potential of improving IL by leveraging diverse data sources through effective data selection.
鏈接:
https://openreview.net/forum?id=vO04AzsB49
?
14.?Can LLM Already Serve as A Database Interface? A BIg Bench for Large-Scale Database Grounded Text-to-SQLs
作者:
Jinyang Li, Binyuan Hui, GE QU, Binhua Li, Jiaxi Yang, Bowen Li, Bailin Wang, Bowen Qin, Ruiying Geng, Nan Huo, Xuanhe Zhou,?Chenhao Ma,?Guoliang Li, Kevin Chang, Fei Huang, Reynold Cheng, Yongbin Li
簡介:
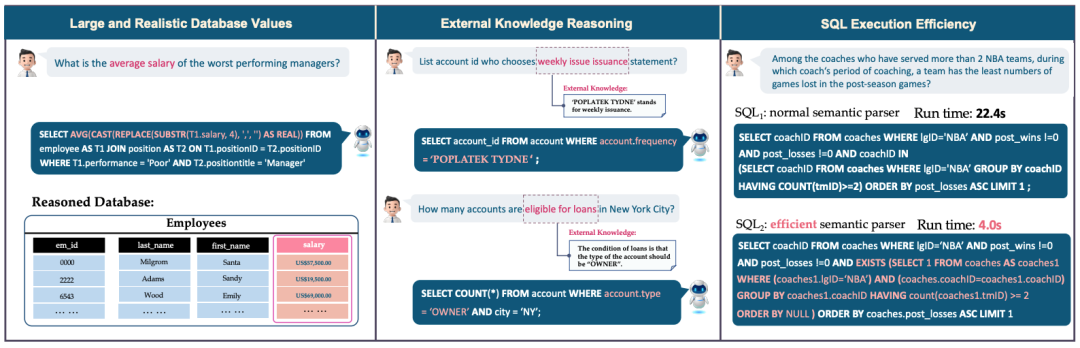
Text-to-SQL解析旨在將自然語言指令轉換為可執行的SQL,在近年來受到了越來越多的關注。特別是Codex和ChatGPT在此任務上展示了令人印象深刻的結果。然而,大多數流行的benchmark,例如Spider和WikiSQL,主要關注具有少量數據庫內容的數據庫模式,這在學術研究和現實世界應用之間留下了差距。為了緩解這一差距,我們提出了Bird,一個大型benchmark,用于大規模數據庫的text-to-SQL任務,其中包含12,751對text-to-SQL數據和95個數據庫,總大小為33.4 GB,橫跨37個專業領域。我們對數據庫值的強調突顯了數據庫內容的新挑戰、NL問題與數據庫內容之間的外部知識以及SQL效率,特別是在大型數據庫的背景下。為了解決這些問題,text-to-SQL模型必須具有數據庫值理解能力,除了語義解析。實驗結果顯示了在為大型數據庫生成準確的text-to-SQLs時,數據庫值的重要性。此外,即使是最有效的text-to-SQL模型,例如ChatGPT,在執行準確性上僅達到40.08%,這仍然遠遠低于人類的92.96%的結果,證明挑戰仍然存在。此外,我們還提供了一個效率分析,為生成對行業有益的text-to-efficient-SQLs提供了見解。我們相信BIRD將有助于推進text-to-SQL研究的實際應用。
Abstracts:
Text-to-SQL parsing, which aims at converting natural language instructions into executable SQLs, has gained increasing attention in recent years. In particular, Codex and ChatGPT have shown impressive results in this task. However, most of the prevalent benchmarks, i.e., Spider, and WikiSQL, focus on database schema with few rows of database contents leaving the gap between academic study and real-world applications. To mitigate this gap, we present Bird, a big benchmark for large-scale database grounded in text-to-SQL tasks, containing 12,751 pairs of text-to-SQL data and 95 databases with a total size of 33.4 GB, spanning 37 professional domains. Our emphasis on database values highlights the new challenges of dirty database contents, external knowledge between NL questions and database contents, and SQL efficiency, particularly in the context of massive databases. To solve these problems, text-to-SQL models must feature database value comprehension in addition to semantic parsing. The experimental results demonstrate the significance of database values in generating accurate text-to-SQLs for big databases. Furthermore, even the most effective text-to-SQL models, i.e. ChatGPT, only achieves 40.08% in execution accuracy, which is still far from the human result of 92.96%, proving that challenges still stand. Besides, we also provide an efficiency analysis to offer insights into generating text-to-efficient-SQLs that are beneficial to industries. We believe that BIRD will contribute to advancing real-world applications of text-to-SQL research.
鏈接:
https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.03111
?
?
15.?Balanced Training for Sparse GANs
作者:
Yite Wang, Jing Wu, Naira Hovakimyan,?Ruoyu Sun
簡介:
在過去的幾年中,人們對開發更大、更深的神經網絡,包括像生成對抗網絡(Generative adversarial networks, GANs)這樣的深度生成模型越來越感興趣。然而,GANs 通常伴隨著高計算復雜度,這使得研究者開始探索降低訓練和推理成本的方法。在監督學習中逐漸受到歡迎的一種方法是動態稀疏訓練(dynamic sparse training, DST),它在稀疏化神經網絡時不僅能夠保持良好性能且享有出色的訓練效率。盡管DST有很多潛在的好處,但由于GANs訓練過程的對抗性,將它應用到GANs還存在著許多挑戰。在本文中,我們提出了一種名為平衡比率(balance ratio, BR)的新指標,用于研究稀疏生成器和鑒別器之間的平衡。我們進一步介紹了一種名為平衡動態稀疏訓練(balanced dynamic sparse training, ADAPT)的新方法,該方法嘗試在GAN訓練中控制BR,很好地實現了稀疏化GANs性能和訓練成本之間的平衡。我們將提出的方法在多個數據集上測試,其優秀的結果證明了ADAPT的有效性。
Abstracts:
Over the past few years, there has been growing interest in developing larger and deeper neural networks, including deep generative models like generative adversarial networks (GANs). However, GANs typically come with high computational complexity,? leading researchers to explore methods for reducing the training and inference costs.? One such approach gaining popularity in supervised learning is dynamic sparse training (DST), which maintains good performance while enjoying excellent training efficiency.? Despite its potential benefits, applying DST to GANs presents challenges due to the adversarial nature of the training process. In this paper, we propose a novel metric called the balance ratio (BR) to study the balance between the sparse generator and discriminator. We also introduce a new method called balanced dynamic sparse training (ADAPT), which seeks to control the BR during GAN training to achieve a good trade-off between performance and computational cost. Our proposed method shows promising results on multiple datasets, demonstrating its effectiveness.
https://neurips.cc/virtual/2023/poster/70078
?
?
16.?Information Design in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
作者:
Yue Lin,?Wenhao Li (SDS博士后),?Hongyuan Zha, Baoxiang Wang
簡介:
強化學習(RL)受到了人類和動物與環境互動的啟發。這種設定有些理想化,因為在實際任務中,環境中的其他智能體有自己的目標,并會根據自我智能體的行為適應性地行動。為了在這些環境中獲得優秀的表現,智能體需要影響其他智能體,使得他的行為變得更有助益且不那么有害。計算經濟學的研究總結了兩種直接影響他人的方法:通過提供有形商品(機制設計)和通過提供信息(信息設計)。這篇工作研究了一組RL智能體的信息設計問題。主要的挑戰有兩方面。一方面是提供的信息會立即影響智能體軌跡的轉換,這引入了額外的非平穩性。另一方面是信息可能會被忽略,所以發送者必須提供接收者愿意尊重的信息。我們制定了馬爾可夫傳信博弈,并發展了傳信梯度和擴展服從約束的概念來應對這些挑戰。我們的算法在各種混合動機任務上都很高效,并為計算經濟學提供了進一步的見解。
Abstracts:
Reinforcement learning (RL) is inspired by how humans and animals interact with the environment. The setting is somewhat idealized because, in actual tasks, other agents in the environment have their own goals and behave adaptively to the ego agent. To thrive in those environments, the agent needs to influence other agents so their actions become more helpful and less harmful. Research in computational economics distills two ways to influence others directly: by providing tangible goods (mechanism design) and by providing information (information design).? This work investigates information design problems for a group of RL agents. The main challenges are two-fold. One is the information provided will immediately affect the transition of the agent trajectories, which introduces additional non-stationarity. The other is the information can be ignored, so the sender must provide information that the receiver is willing to respect. We formulate the Markov signaling game, and develop the notions of signaling gradient and the extended obedience constraints that address these challenges. Our algorithm is efficient on various mixed-motive tasks and provides further insights into computational economics.?
https://github.com/YueLin301/InformationDesignMARL
?
?
17.?Learning Adversarial Low-rank Markov Decision Processes with Unknown Transition and Full-information Feedback
作者:
Canzhe Zhao, Ruofeng Yang,?Baoxiang Wang,?Xuezhou Zhang, Shuai Li
簡介:
我們研究了在全信息反饋設置下的對抗性低秩馬爾可夫決策過程. 這個設定下, 轉移概率函數時未知的, 并且存在低秩矩陣分解, 同時損失函數可能會發生對抗性變化, 但會在每次迭代之后向學習者揭示。我們提出了一種基于策略優化的算法, POLO, 并證明它達到了 $\widetilde{O}\left(\frac{K^{\frac{3}{4}} A^{\frac{1}{ 2}} d\ln^{\frac{1}{4}}M}{1-\gamma}+\frac{\sqrt{K}}{(1-\gamma)^2}\right)$的后悔界, 其中 $d$ 是轉移矩陣的秩, $A$ 是動作空間的大小,$M$ 是模型集合的大小, $\gamma$是折扣因子. 值得注意的是,我們的算法調用orcale次數較低, 并且后悔界與狀態集大小無關. 據我們所知, 這是第一個結合了表示學習, 探索和利用的平衡, 以實現具有非線性函數逼近和對抗性損失的強化學習的次線性后悔保證。
Abstracts:
In this work, we study the low-rank MDPs with adversarially changed losses in the full-information feedback setting. In particular, the unknown transition probability function admits a low-rank matrix decomposition \citep{REPUCB22}, and the loss functions may change adversarially but are revealed to the learner at the end of each episode. We propose a policy optimization-based algorithm POLO, and we prove that it attains the $\widetilde{O}\left(\frac{K^{\frac{3}{4}}? ?A^{\frac{1}{2}} d\ln^{\frac{1}{4}}M}{1-\gamma}+\frac{\sqrt{K}}{(1-\gamma)^2}\right)$ regret guarantee, where $d$ is rank of the transition kernel (and hence the dimension of the unknown representations), $A$ is the cardinality of the action space, $M$ is the cardinality of the model class, and $\gamma$ is the discounted factor. Notably, our algorithm is oracle-efficient and has a regret guarantee with no dependence on the size of potentially arbitrarily large state space. To the best of our knowledge, we present the first algorithm that interleaves representation learning, exploration, and exploitation to achieve the sublinear regret guarantee for RL with nonlinear function approximation and adversarial losses.
?
?
18.?Two Heads are Better Than One: A Simple Exploration Framework for Efficient Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
作者:
Jiahui Li, Kun Kuang,?Baoxiang Wang,?Xingchen Li, Long Chen, Fei Wu, Jun Xiao
簡介:
探索策略在強化學習中發揮著重要作用,尤其是在稀疏獎勵任務中。在協作多智能體強化學習(MARL)中,由于狀態空間大和智能體之間復雜的交互,設計合適的探索策略更具挑戰性。目前,MARL中的主流探索方法要么有助于探索大而稀疏的陌生狀態,要么以高計算成本測量智能體之間的交互。我們發現一個有趣的現象,不同類型的探索在不同的MARL場景中發揮著不同的作用,選擇合適的探索往往比設計精致的算法更有效。在本文中,我們提出了一種結合基于好奇心和基于影響力的探索(COIN)的探索方法,該方法簡單但在各種情況下都有效。首先,COIN 基于互信息理論衡量每個智能體對其他智能體的影響,并將其設計為應用于每個個體價值函數的內在獎勵。此外,COIN 通過添加到外在獎勵中的預測誤差來計算基于好奇心的內在獎勵。為了整合這兩種內在獎勵,COIN 采用了一種新穎的框架,使它們相互補充,并對合作 MARL 任務進行了充分有效的探索。我們對三個具有挑戰性的基準進行了廣泛的實驗:星際爭霸 II、MACO 和 Google Football。不同場景的結果顯示了我們 COIN 的優越性。
Abstracts:
Exploration strategy plays an important role in reinforcement learning, especially in sparse-reward tasks. In cooperative multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL), designing a suitable exploration strategy is much more challenging due to the large state space and the complex interaction among agents. Currently, mainstream exploration methods in MARL either contribute to exploring the unfamiliar states which are large and sparse, or measuring the interaction among agents with high computational costs. We found an interesting phenomenon that different kinds of exploration plays a different role in different MARL scenarios, and choosing a suitable one is often more effective than designing an exquisite algorithm. In this paper, we propose a exploration method that incorporate the curiosity-based and influence-based exploration (COIN) which is simple but effective in various situations. First, COIN measures the influence of each agent on the other agents based on mutual information theory and designs it as intrinsic rewards which are applied to each individual value function. Moreover, COIN computes the curiosity-based intrinsic rewards via prediction errors which are added to the extrinsic reward. For integrating the two kinds of intrinsic rewards, COIN utilizes a novel framework in which they complement each other and lead to a sufficient and effective exploration on cooperative MARL tasks. We perform extensive experiments on three challenging benchmarks: StarCraft II, MACO, and Google Football. The results across different scenarios show the superiority of our COIN.
?
?
19.??Med-UniC: Unifying Cross-Lingual Medical Vision-Language Pre-Training by Diminishing Bias
作者:
Zhongwei Wan, Che Liu, Mi Zhang, Jie Fu,?Benyou Wang,?Sibo Cheng, Lei Ma, César Quilodrán-Casas, Rossella Arcucc
簡介:
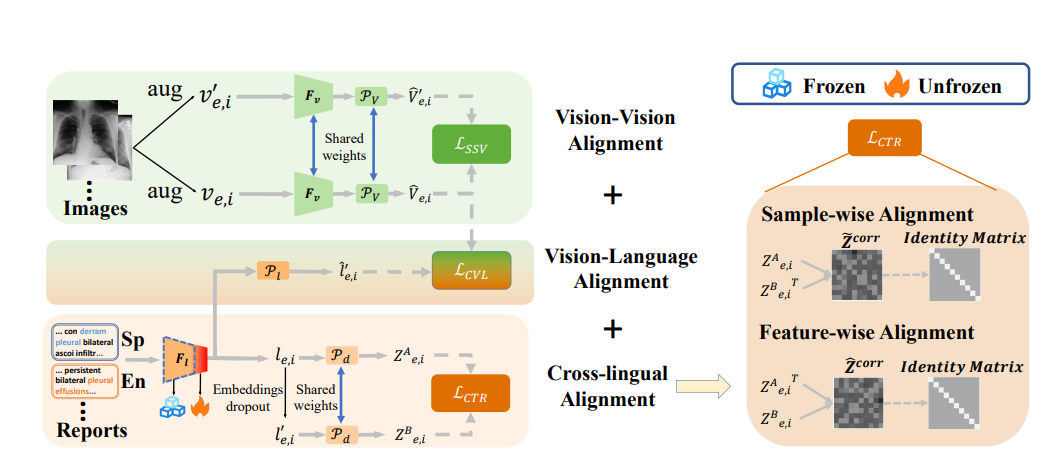
數據稀缺是醫學視覺-語言預訓練(VLP)有效性的一個關鍵障礙。一個可能的解決方案是結合來自不同語言社區的數據集。然而,主要的挑戰來自于整合多樣的語法和語義、特定于語言的醫學術語以及特定于文化的隱式知識的復雜性。因此,考慮的一個關鍵方面是由于不同語言而產生的社區偏見。本文提出了一個名為統一跨語言醫學視覺-語言預訓練(Med-UniC)的新框架,旨在整合來自英語和西班牙語這兩種最普遍的語言的多模態醫學數據。具體來說,我們提出了CTR(跨語言文本對齊規范化)來明確地統一來自不同語言社區的醫學報告的跨語言語義表示。通過潛在語言的解纏,優化了CTR,使我們的優化目標不依賴于負樣本,從而顯著減少了在類似的醫學報告中確定正負樣本對的偏見。此外,它確保了跨語言表示不偏向于任何特定的語言社區。Med-UniC在5個醫學圖像任務和10個數據集中達到了卓越的性能,涵蓋了30多種疾病,為統一多模態醫學數據提供了一個多功能的框架,適用于不同的語言社區。實驗結果突顯了跨語言VLP中社區偏見的存在。減少這種偏見不僅提高了視覺-語言任務的性能,而且提高了單一模式的視覺任務的性能。
Abstracts:
The scarcity of data presents a critical obstacle to the efficacy of medical vision-language pre-training (VLP). A potential solution lies in the combination of datasets from various language communities. Nevertheless, the main challenge stems from the complexity of integrating diverse syntax and semantics, language-specific medical terminology, and culture-specific implicit knowledge. Therefore, one crucial aspect to consider is the presence of community bias caused by different languages. This paper presents a novel framework named Unifying Cross-Lingual Medical Vision-Language Pre-Training (\textbf{Med-UniC}), designed to integrate multi-modal medical data from the two most prevalent languages, English and Spanish. Specifically, we propose \textbf{C}ross-lingual \textbf{T}ext Alignment \textbf{R}egularization (\textbf{CTR}) to explicitly unify cross-lingual semantic representations of medical reports originating from diverse language communities. \textbf{CTR} is optimized through latent language disentanglement, rendering our optimization objective to not depend on negative samples, thereby significantly mitigating the bias from determining positive-negative sample pairs within analogous medical reports. Furthermore, it ensures that the cross-lingual representation is not biased toward any specific language community. \textbf{Med-UniC} reaches superior performance across 5 medical image tasks and 10 datasets encompassing over 30 diseases, offering a versatile framework for unifying multi-modal medical data within diverse linguistic communities. The experimental outcomes highlight the presence of community bias in cross-lingual VLP. Reducing this bias enhances the performance not only in vision-language tasks but also in uni-modal visual tasks.
鏈接:
https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.19894
?
?
20.??All In One A Chinese Multi-Modal Dataset for Multi-Affection Detection in Conversations
作者:
Yazhou Zhang, Yang Yu, Qing Guo,?Benyou Wang,?Dongming Zhao, Sagar Uprety, Dawei Song, Jing Qin, Qiuchi Li
簡介:
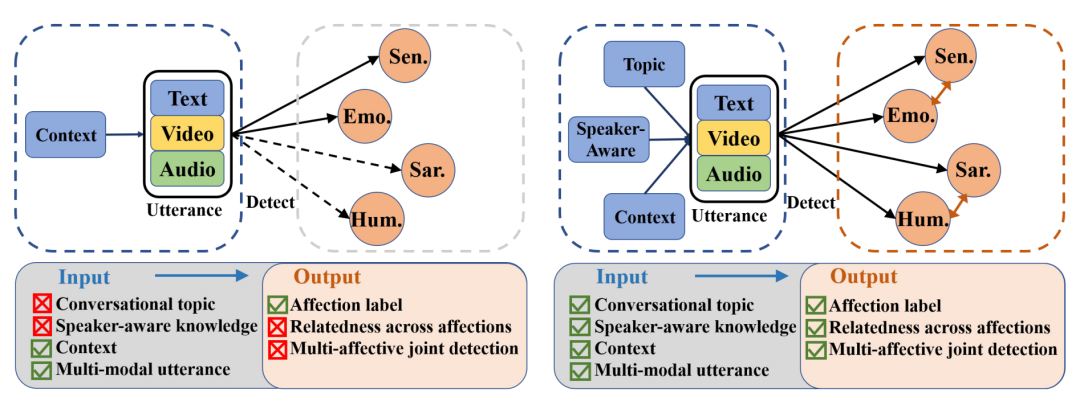
人類的交流具有多模態和多情感的特性。不同情感和情緒之間的相互關系使得利用多模態線索共同檢測多種人類情感面臨挑戰。最近在這個領域的進展采用了多任務學習范式,以實現任務之間的相互關系,但是公開資源的稀缺性限制了這方面工作的潛力。為了填補這一空白,我們構建了第一個中文多模態多情感對話(CMMA)數據集,其中包含了3,000個多方對話和來自各種電視劇風格的21,795個多模態話語。CMMA包含了各種各樣的情感標簽,包括情緒、情感、諷刺和幽默,以及某些任務對之間的新穎相互關系數值。此外,它還提供了對話中的話題和發言者信息,促進了對話背景的更好建模。在這個數據集上,我們經驗性地分析了不同數據模態和對話背景對不同情感分析任務的影響,并展示了任務間關聯的實際益處。
Abstracts:
Human communication has a multi-modal and multi-affection nature. The inter-relatedness of different emotions and sentiments poses a challenge to jointly detect multiple human affections with multi-modal clues. Recent advances in this field employed multi-task learning paradigms to render the inter-relatedness across tasks, but the scarcity of publicly available resources sets a limit to the potential of works. To fill this gap, we build the first Chinese Multi-modal Multi-Affection conversation (CMMA) dataset, which contains 3,000 multi-party conversations and 21,795 multi-modal utterances collected from various styles of TV-series. CMMA contains a wide variety of affection labels, including sentiment, emotion, sarcasm and humor, as well as the novel inter-correlations values between certain pairs of tasks. Moreover, it provides the topic and speaker information in conversations, which promotes better modeling of conversational context. On the dataset, we empirically analyze the influence of different data modalities and conversational contexts on different affection analysis tasks, and exhibit the practical benefit of inter-task correlations.
鏈接:
https://neurips.cc/virtual/2023/poster/73481
?
?
21.?DeepfakeBench: A Comprehensive Benchmark of Deepfake Detection
作者:
Zhiyuan Yan (SDS碩士生),Yong Zhang, Xinhang Yuan, Siwei Lyu,?Baoyuan Wu
簡介:
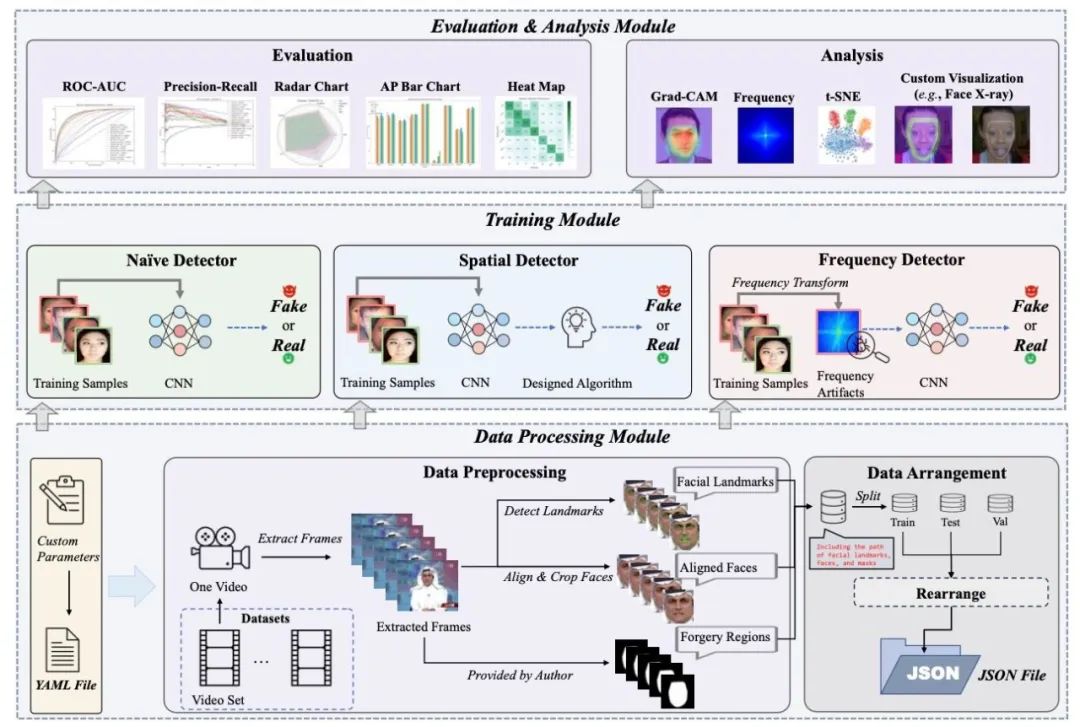
Deepfake檢測領域的一個關鍵但常被忽視的挑戰是:缺乏標準化、統一、全面的基準。這會導致不公平的性能比較和潛在的誤導性結果。具體來說,數據處理流程缺乏統一性,導致輸入每個檢測模型的數據不統一。此外,不同方法的實驗設置存在明顯差異,評估策略和指標也普遍缺乏標準化。為了填補這一空白,我們提出了領域內第一個用于 Deepfake檢測的綜合基準,稱為DeepfakeBench,它提供了三個關鍵貢獻:1)統一的數據管理系統,以確保所有檢測器的輸入一致,2)針對最新的SOTA方法集成的一套統一訓練框架,以及3)標準化的評估指標和協議,以提高透明度和可重復性。DeepfakeBench具有可擴展、模塊化的代碼庫,包含15種最先進的檢測方法、9個deepfake數據集、一系列deepfake檢測評估協議和分析工具以及綜合評估。此外,我們根據從不同角度(例如數據增強、骨干網絡)基于這些評估進行了廣泛分析并提供了新的見解。我們希望我們的努力能夠促進未來的研究并促進這個日益重要的領域的創新。?
Abstracts:
A critical yet frequently overlooked challenge in the field of deepfake detection is the lack of a standardized, unified, comprehensive benchmark. This issue leads to unfair performance comparisons and potentially misleading results. Specifically, there is a lack of uniformity in data processing pipelines, resulting in inconsistent data inputs for detection models. Additionally, there are noticeable differences in experimental settings, and evaluation strategies and metrics lack standardization. To fill this gap, we present the first comprehensive benchmark for deepfake detection, called DeepfakeBench, which offers three key contributions: 1) a unified data management system to ensure consistent input across all detectors, 2) an integrated framework for state-of-the-art methods implementation, and 3) standardized evaluation metrics and protocols to promote transparency and reproducibility. Featuring an extensible, modular-based codebase, DeepfakeBench contains 15 state-of-the-art detection methods, 9 deepfake datasets, a series of deepfake detection evaluation protocols and analysis tools, as well as comprehensive evaluations. Moreover, we provide new insights based on extensive analysis of these evaluations from various perspectives (e.g., data augmentations, backbones). We hope that our efforts could facilitate future research and foster innovation in this increasingly critical domain. All codes, evaluations, and analyses of our benchmark are publicly available at this https URL.
鏈接:
https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.01426
?
?
22.?Shared Adversarial Unlearning: Backdoor Mitigation by Unlearning Shared Adversarial Examples
作者:
Shaokui Wei (SDS博士生), Mingda Zhang (SDS博士生), Hongyuan Zha, Baoyuan Wu?
簡介:
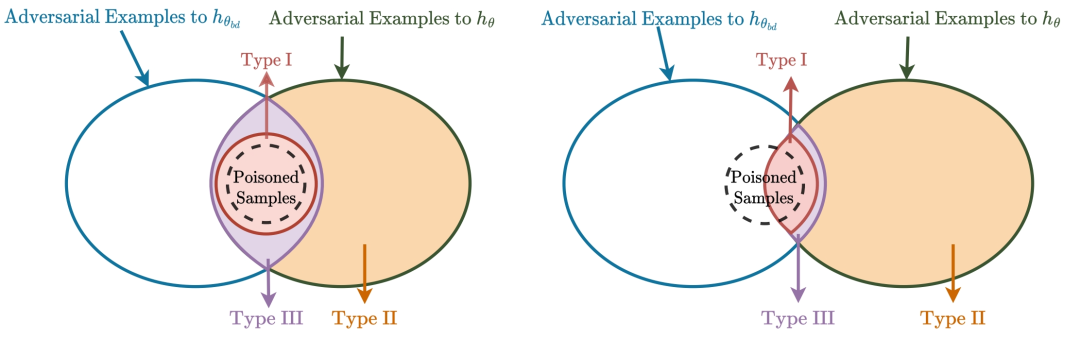
后門攻擊是機器學習的重大安全威脅,對手可以將帶有觸發器的樣本注入訓練集,從而訓練一個后門模型,該模型可以預測帶有特定觸發器的樣本到特定的目標類別,而在良性樣本上表現正常。在這篇論文中,我們探索了使用小的干凈數據集凈化后門模型的任務。通過建立后門風險和對抗風險之間的聯系,我們推導出了一個新穎的后門風險上界,其主要捕捉了后門模型和凈化模型之間的共享對抗樣本(SAEs)的風險。這個上界進一步提出了一種新穎的雙層優化問題,用于利用對抗訓練技術減輕后門的影響。為了解決這個問題,我們提出了共享對抗反學習(SAU)。具體而言,SAU首先生成SAEs,然后反學習生成的SAEs,以便它們被凈化模型正確分類或由兩個模型以不同的方式分類,從而在凈化模型中減輕后門的影響。在各種基準數據集和網絡架構上的實驗表明,我們提出的方法在后門防御方面達到了最先進的性能。
Abstracts:
Backdoor attacks are serious security threats to machine learning models where an adversary can inject poisoned samples into the training set, causing a backdoored model which predicts poisoned samples with particular triggers to particular target classes, while behaving normally on benign samples. In this paper, we explore the task of purifying a backdoored model using a small clean dataset. By establishing the connection between backdoor risk and adversarial risk, we derive a novel upper bound for backdoor risk, which mainly captures the risk on the shared adversarial examples (SAEs) between the backdoored model and the purified model. This upper bound further suggests a novel bi-level optimization problem for mitigating backdoor using adversarial training techniques. To solve it, we propose Shared Adversarial Unlearning (SAU). Specifically, SAU first generates SAEs, and then, unlearns the generated SAEs such that they are either correctly classified by the purified model and/or differently classified by the two models, such that the backdoor effect in the backdoored model will be mitigated in the purified model. Experiments on various benchmark datasets and network architectures show that our proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance for backdoor defense.
鏈接:
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2307.10562
?
23.?Neural Polarizer: A Lightweight and Effective Backdoor Defense via Purifying Poisoned Features
作者:
Mingli Zhu (SDS博士生), Shaokui Wei (SDS博士生), Hongyuan Zha, Baoyuan Wu
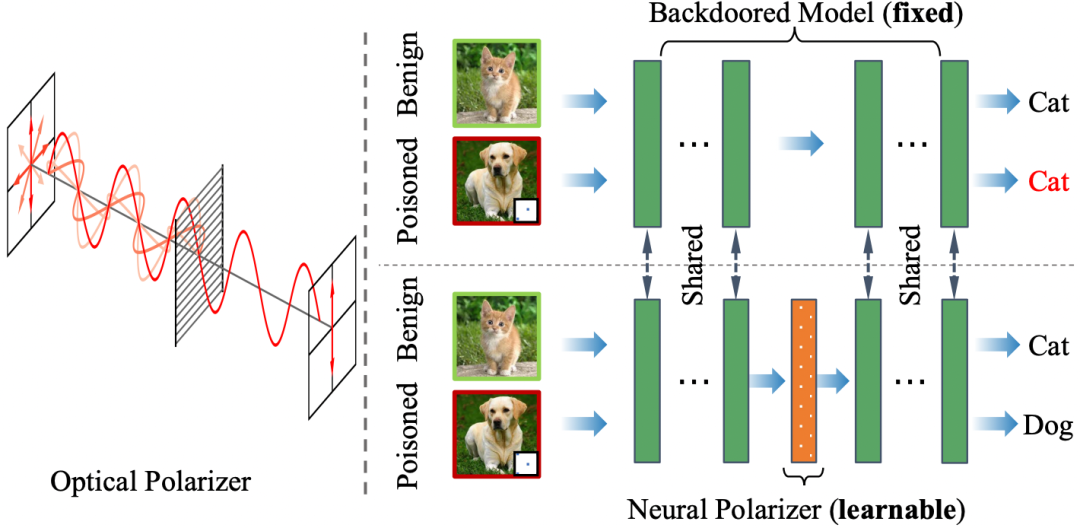
簡介:
最近的研究證明了深度神經網絡對后門攻擊的敏感性。給定一個后門模型,盡管觸發器信息和良性信息共存,但其對具有觸發的中毒樣本的預測將由觸發信息主導。受光學偏振器機制的啟發,偏振器可以通過特定偏振的光波,同時過濾其他偏振的光波,我們提出了一種新穎的后門防御方法,通過在后門模型中插入可學習的神經偏振器作為中間層,以便通過過濾觸發信息來凈化中毒樣本,同時保持良性信息。神經偏振器被實例化為一個輕量級線性變換層,它是通過基于有限的干凈數據集解決精心設計的雙層優化問題來學習的。與其他經常調整后門模型所有參數的基于微調的防御方法相比,所提出的方法只需要額外學習一層,因此效率更高,并且需要更少的干凈數據。大量的實驗證明了我們的方法在消除各種神經網絡架構和數據集中的后門方面的有效性和效率,特別是在干凈數據非常有限的情況下。
Abstracts:
Recent studies have demonstrated the susceptibility of deep neural networks to backdoor attacks. Given a backdoored model, its prediction of a poisoned sample with trigger will be dominated by the trigger information, though trigger information and benign information coexist. Inspired by the mechanism of the optical polarizer that a polarizer could pass light waves with particular polarizations while filtering light waves with other polarizations, we propose a novel backdoor defense method by inserting a learnable neural polarizer into the backdoored model as an intermediate layer, in order to purify the poisoned sample via filtering trigger information while maintaining benign information. The neural polarizer is instantiated as one lightweight linear transformation layer, which is learned through solving a well designed bi-level optimization problem, based on a limited clean dataset. Compared to other fine-tuning-based defense methods which often adjust all parameters of the backdoored model, the proposed method only needs to learn one additional layer, such that it is more efficient and requires less clean data. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of our method in removing backdoors across various neural network architectures and datasets, especially in the case of very limited clean data.
鏈接:
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2306.16697.pdf
?
24.?AUDIT: Audio Editing by Following Instructions with Latent Diffusion Models
作者:
Yuancheng Wang (SDS博士生),?Zeqian Ju, Xu Tan, Lei He,?Zhizheng Wu,?Jiang Bian,?Sheng Zhao
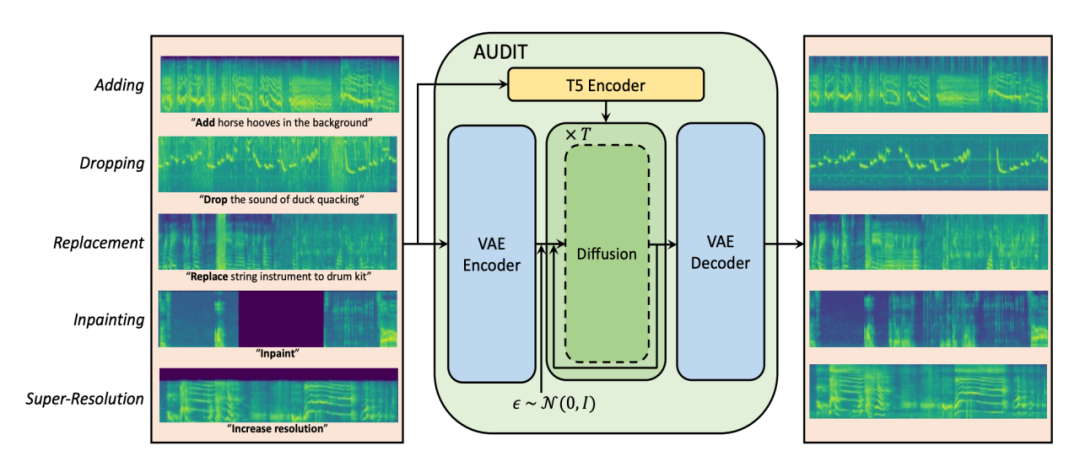
簡介:
音頻編輯適用于多種目的,例如添加背景音效、替換樂器伴奏或者修復損壞的音頻。最近,一些基于深度擴散模型的方法通過使用以輸出音頻的文本描述為條件的擴散和去噪過程實現了零樣本音頻編輯。然而,這些方法仍然存在一些問題:1)它們沒有經過編輯任務的訓練,無法保證良好的編輯效果;2)他們可能會錯誤地修改不需要編輯的音頻片段;3)他們需要輸出音頻的完整描述,這在實際場景中并不總是可用或必需的。在這項工作中,我們提出了 AUDIT,一種基于潛在擴散模型的指令引導音頻編輯模型。具體來說,AUDIT具有三個主要設計特點:1)我們為不同的音頻編輯任務構建三元組訓練數據(指令、輸入音頻、輸出音頻),并使用指令和輸入(待編輯)音頻作為條件訓練擴散模型并生成輸出 (編輯)音頻;2)通過比較輸入和輸出音頻的差異,自動學習只修改需要編輯的片段;3)只需要編輯指令,而不需要完整的目標音頻描述作為文本輸入。AUDIT 在多個音頻編輯任務(例如添加、刪除、替換、修復、超分辨率)的客觀和主觀指標方面均取得了最先進的結果。
Abstracts:
Audio editing is applicable for various purposes, such as adding background sound effects, replacing a musical instrument, and repairing damaged audio. Recently, some diffusion-based methods achieved zero-shot audio editing by using a diffusion and denoising process conditioned on the text description of the output audio. However, these methods still have some problems: 1) they have not been trained on editing tasks and cannot ensure good editing effects; 2) they can erroneously modify audio segments that do not require editing; 3) they need a complete description of the output audio, which is not always available or necessary in practical scenarios. In this work, we propose AUDIT, an instruction-guided audio editing model based on latent diffusion models. Specifically, AUDIT has three main design features: 1) we construct triplet training data (instruction, input audio, output audio) for different audio editing tasks and train a diffusion model using instruction and input (to be edited) audio as conditions and generating output (edited) audio; 2) it can automatically learn to only modify segments that need to be edited by comparing the difference between the input and output audio; 3) it only needs edit instructions instead of full target audio descriptions as text input. AUDIT achieves state-of-the-art results in both objective and subjective metrics for several audio editing tasks (e.g., adding, dropping, replacement, inpainting, super-resolution).
鏈接:
https://arxiv.org/abs/2304.00830
?
25.?Motion-X A Large-scale 3D Expressive Whole-body Human Motion Dataset
作者:
Jing Lin, Ailing Zeng,?Shunlin Lu (SDS 博士生),?Yuanhao Cai,?Ruimao Zhang,?Haoqian Wang, Lei Zhang
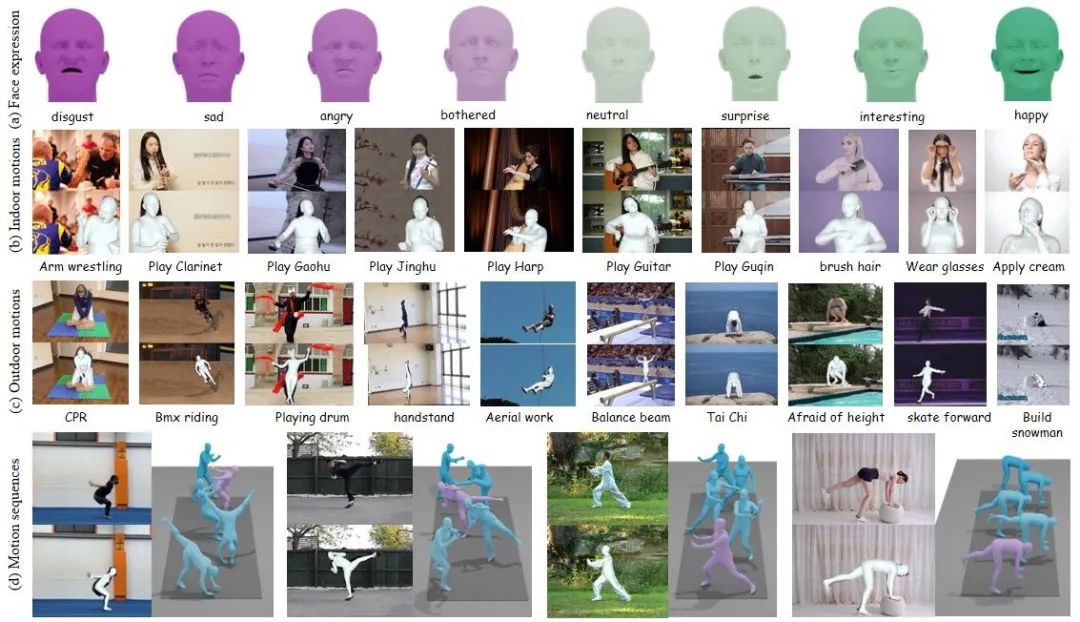
簡介:
在本文中,我們提出了Motion-X,這是一個大規模的3D表情全身運動數據集。現有的運動數據集主要包含僅限于身體的姿勢,缺少面部表情、手勢和詳細的姿勢描述。而且,這些數據集主要是在實驗室環境中以手工標注文本描述的方式收集而來,這大大限制了它們的可擴展性。為了克服這些限制,我們開發了一個全身運動和文本注釋流程,它可以自動注釋來自單視圖或多視圖視頻的運動,并為每個視頻提供全面的語義標簽,以及為每個幀提供詳細的全身姿勢描述。這個流程具有高精度、成本效益,并且可擴展,適用于進一步的研究。基于此,我們構建了Motion-X,它包含了1370萬精確的3D全身姿勢注釋(即SMPL-X),涵蓋了來自大量場景的96K運動序列。此外,Motion-X還提供了1370萬幀級全身姿勢描述和96K序列級語義標簽。全面的實驗驗證了注釋流程的準確性,以及Motion-X在增強表情豐富、多樣化和自然運動生成以及3D全身人體網格恢復方面的顯著優勢。
Abstracts:
In this paper, we present Motion-X, a large-scale 3D expressive whole-body motion dataset. Existing motion datasets predominantly contain body-only poses, lacking facial expressions, hand gestures, and fine-grained pose descriptions. Moreover, they are primarily collected from limited laboratory scenes with textual descriptions manually labeled, which greatly limits their scalability. To overcome these limitations, we develop a whole-body motion and text annotation pipeline, which can automatically annotate motion from either single- or multi-view videos and provide comprehensive semantic labels for each video and fine-grained whole-body pose descriptions for each frame. This pipeline is of high precision, cost-effective, and scalable for further research. Based on it, we construct Motion-X, which comprises 13.7M precise 3D whole-body pose annotations (i.e., SMPL-X) covering 96K motion sequences from massive scenes. Besides, Motion-X provides 13.7M frame-level whole-body pose descriptions and 96K sequence-level semantic labels. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate the accuracy of the annotation pipeline and the significant benefit of Motion-X in enhancing expressive, diverse,and natural motion generation, as well as 3D whole-body human mesh recovery.
鏈接:
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2307.00818.pdf
?
26.?A Batch-to-Online Transformation under Random-Order Model
作者:
Jing Dong(SDS博士生),Yuichi Yoshida
簡介:
我們介紹了一個轉換框架,可用于開發低功耗在線算法通過離線近似算法在隨機順序模型中近似后悔。我們首先給出一個通用歸約定理,將具有低平均靈敏度的離線近似算法轉換為具有低近似遺憾的在線算法。然后,我們證明可以使用核心集構造方法將離線近似算法轉換為低靈敏度版本。為了展示我們方法的多功能性,我們將其應用于各種問題,包括在線聚類、在線矩陣近似和在線回歸,并成功實現每個問題的多對數近似后悔。此外,我們表明,在所有三種情況下,我們的算法也具有較低的不一致性,這在某些在線應用程序中可能是需要的。
Abstracts:
We introduce a transformation framework that can be utilized to develop online algorithms with low?
approximate regret in the random-order model from offline approximation algorithms. We first give a general reduction theorem that transforms an offline approximation algorithm with low average sensitivity to an online algorithm with low approximate regret. We then demonstrate that offline approximation algorithms can be transformed into a low-sensitivity version using a coreset construction method. To showcase the versatility of our approach, we apply it to various problems, including online clustering, online matrix approximation, and online regression, and successfully achieve polylogarithmic approximate regret for each problem. Moreover, we show that in all three cases, our algorithm also enjoys low inconsistency, which may be desired in some online applications.
https://openreview.net/forum?id=B6HSIgvyJ3&referrer=%5BAuthor%20Console%5D(%2Fgroup%3Fid%3DNeurIPS.cc%2F2023%2FConference%2FAuthors%23your-submissions)
?





